

The compartmentalization of body fluids was measured in individual Pekin ducks ( Anas platyrhynchos) drinking freshwater and after sequential acclimation to 300 mM NaCl and 400 mM NaCl. The point is made that the kidney regulates the volume and composition of body fluids by operating on the plasma. The rest of the chapter considers the effects of three interventions on the intracellular and extracellular fluid volumes and osmolarity: drinking 1 L of water eating 10 g of NaCl, and infusing 1 L of isotonic saline.

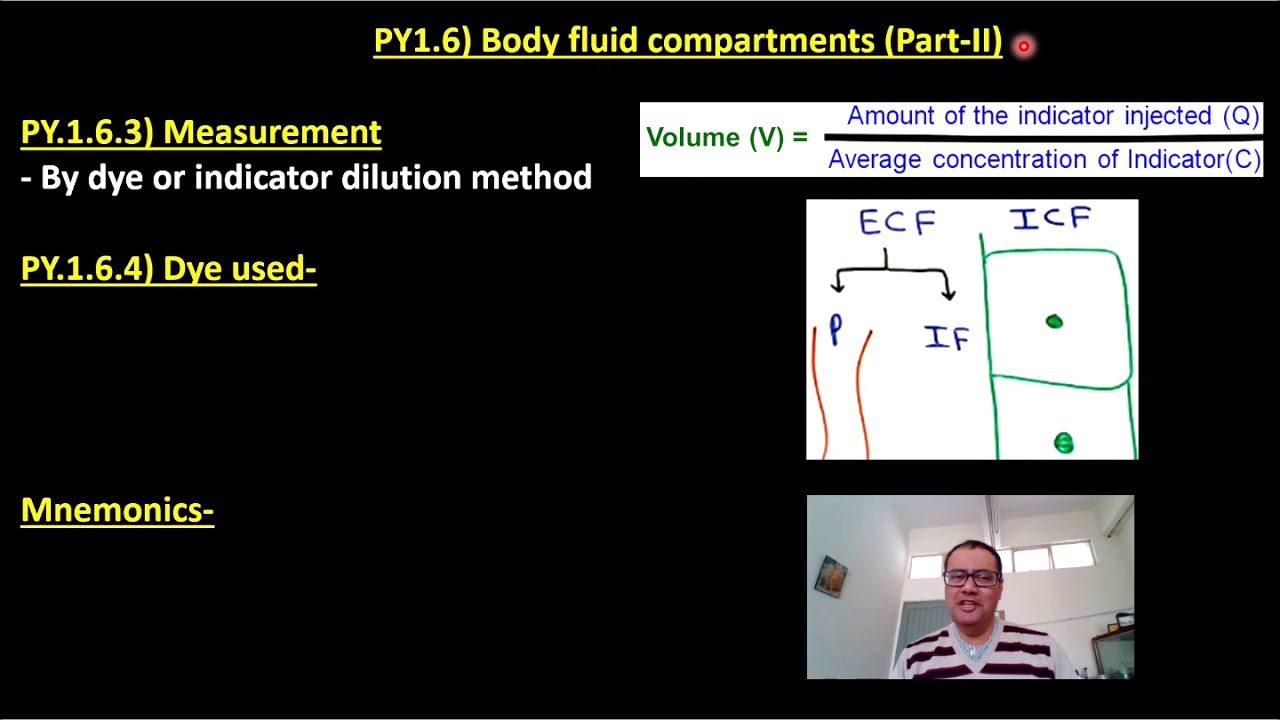
The basis of the Gibbs–Donnan distribution ratio is discussed. The plasma and ISF are nearly identical except for the protein concentration and its attendant Gibbs–Donnan effect. The main fluid compartments are not these, but the intracellular fluid, interstitial fluid (ISF), and plasma, which can be obtained from the volumes of distribution of these markers. The plasma volume can be found using Evan’s blue dye as a marker, and it is typically 5% of body weight. The extracellular volume can be determined by inulin as a marker, and it averages 20% of body weight. Total body water is marked by deuterium oxide and averages around 60% of body weight. This chapter describes the indicator dilution method for determining the volume of distribution of otherwise inaccessible fluid compartments.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
